COLFIO Docs
- documentation to the
COLFIOlibrary that can be found in the repository
Pixi architecture

COLFIO Library
- a minimalist library for NI-APH that implements ECS pattern with the most important amenities
- located in
examples/libs/pixi-ecs - features
- object builder
- scene manager
- PIXI-ECS bridging
- messaging pattern
- reactive components
- states, flags and tags
- simple debugging window
- keyboard/pointer handlers
Architecture
- PIXI.Application
- PIXI application
- PIXI.Ticker
- PIXI clock for game loop
- PIXI.Container, PIXI.Sprite,...
- PIXI game objects
- ECS.Engine
- entry point to the library, accepts a configuration object and initializes PIXI game loop
- ECS.Scene
- a scene manager, provides querying of components and game objects, manages global components
- ECS.Component
- functional components of game objects
- global components are attached to the
stageobject
- ECS.GameObject
- an interface that declares extension methods for PIXI containers
- in older versions, all components and the
Sceneworked with the containers throughGameObjectinterface and accessing PIXI attributes required to use casting functions such as ˙asContainer()˙. The current version uses inherited ˙ECS.Container˙, so that it is possible to access bothECSandPIXIfunctions at the same time.GameObjectinterface is now only used internally for derived objects to force them to implement allECSfunctions
- ECS.GameObjectProxy
- a delegate that contains implementation of methods in
ECS.GameObjectinterface. It's used as a proxy by respective containers (because JavaScript doesn't have multi-inheritance facility)
- a delegate that contains implementation of methods in
- ECS.Container, ECS.Sprite,...
- PIXI containers that inherits from respective PIXI objects, implements
ECS.GameObjectinterface and passes the implementation on toECS.GameObjectProxy(in order to avoid duplicated code)
- PIXI containers that inherits from respective PIXI objects, implements

COLFIO binding
- instead of creating
PIXI.Container,PIXI.Spriteetc., we can createECS.Container,ECS.Sprite,... - those objects inherit from their respective counterparts in PIXI. Additionally, they contain methods from
ECS.GameObjectinterface - they can be treated in the same way as regular PIXI objects
- they use
GameObjectProxyas a provider of the implementation of ECS features - any functional behaviour can be implemented in components, having them manipulate with game objects they are attached to

How to start
- import the ECS library
- get your canvas
- call the
initfunction - load your resources by using
PIXI loader - access the
engine.scene
import * as ECS from '../libs/pixi-ecs';
class MyGame {
engine: ECS.Engine;
constructor() {
this.engine = new ECS.Engine();
let canvas = (document.getElementById('gameCanvas') as HTMLCanvasElement);
this.engine.init(canvas, { width: 800, height: 600 });
this.engine.app.loader
.reset()
.add('spritesheet', './assets/spritesheet.png')
.load(onAssetsLoaded);
}
onAssetsLoaded = () => {
this.engine.scene.clearScene();
const graphics = new ECS.Graphics();
this.engine.scene.stage.addChild(graphics);
}
}
export default new MyGame();
engine.appis a link toPIXI.Applicationscene.stageis a link to the stage object in PIXIscene.stage.addChild(...)allows us to add children to the stage object
let sprite = new ECS.Sprite('mySprite', PIXI.Texture.from('spritesheet'));
sprite.position.set(engine.app.screen.width / 2, engine.app.screen.height / 2);
sprite.anchor.set(0.5);
engine.scene.stage.addChild(sprite);
Config
- to optimize query search in the scene, all components and objects are stored in hash maps, sets and array
- in order not to allocate too much memory, searching has to be enabled explicitly
- don't worry! If you forget to enable it, it will inform you via an Error thrown 🤣
new ECS.Engine().init(canvas, {
width: 800,
height: 600,
debugEnabled: true,
flagsSearchEnabled: true,
statesSearchEnabled: true,
}, true);
resizeToScreen- if true, the game will be resized to fit the screentransparent- if true, the canvas will be trasparentbackgroundColor- canvas background colorantialias- enables antialiasingwidth- canvas virtual widthheight- canvas virtual heightresolution- scale of displayed objects (1 by default)gameLoopType- type of the game loop (FIXED, VARIABLE)gameLoopThreshold- upper threshold of game loop in ms (300 by default)gameLoopFixedTick- period for fixed game loop (16ms by default)speed- speed of the game (1 by default)flagsSearchEnabled- enables searching by flagsstatesSearchEnabled- enables searching by statestagsSearchEnabled- enables searching by tagsnamesSearchEnabled- enables searching by namesnotifyAttributeChanges- enables notifying when an attribute changesnotifyStateChanges- enables notifying when a state changesnotifyFlagChanges- enables notifying when a flag changesnotifyTagChanges- enables notifying when a tag changesdebugEnabled- injects a debugging HTML element
Components
- every functional behavior is implemented in components
- every component is attached to one game object
- global components are attached directly to the stage

id- unique identifiername- component nameprops- custom property object (void by default)owner- game object this component is attached toscene- link to the scenefixedFrequency- frequency of the fixed udpate loop (if unset, fixedUpdate() will NOT be invoked)cmpState- component state (NEW, INITIALIZED, RUNNING, DETACHED, FINISHED)onInit()- called when the component is added to an objectonAttach()- called when the component is attached to the sceneonMessage()- called whenever a message the component has subscribed to arrivesonFixedUpdate()- called at a fixed intervalonUpdate()- called every frameonDetach()- called before the component is detached from the sceneonRemove()- called before the component is removed from the sceneonFinish()- called whenever someone calls 'finish()', followed by removing from the scenesubscribe()- subscribes for a message of a given keyunsubscribe()- unsubscribes a message of a given keysendMessage()- sends a messagefinish()- cancels the execution of the component and removes it from the scene instantly
A simple component
- create a new component
- initialize it in
onInit() - handle incoming messages in
onMessage() - handle update loop in
onUpdate(delta, absolute)
class Movement extends ECS.Component {
onInit() {
this.subscribe('STOP_EVERYTHING');
}
onMessage(msg: ECS.Message) {
if(msg.action === 'STOP_EVERYTHING') {
this.finish();
}
}
onUpdate(delta: number, absolute: number) {
this.owner.pos.set(this.owner.pos.x + 20, this.owner.pos.y);
}
}
Lifecycle
- components are not added to objects instantly, but at the beginning of the update loop of their respective objects
- immediate execution can be forced by calling
addComponentAndRuninstead ofaddComponent
- immediate execution can be forced by calling
- components can be reused - removed from an object and added to another one
- a component can be only attached to one game object at a time
- components can receive messages if they are running
- components can't receive message they had sent by themselves
finish()will stop the components from execution and removes it from the scene- if a game object is to be removed, all of its components will be finalized and removed as well
- if the parent game object gets detached from the scene (e.g. for later reuse), all of its components will be also detached and re-attached afterwards
onAttach()is called when a component is attached to the scene. It can happen in two cases:- a) component is added to an object that is already on the scene
- b) a game object is attached to a scene (so will be its components)
- if the component is detached, it won't update nor receive any messages
- recommended: if you don't need to react on detaching, use only
onInit()for initialization andonRemove()for clean-up

Game Object
- game object is a class inherited from respective PIXI containers (Container, Sprite, Text, Mesh,...)

id- unique identifiername- name (empty string by default)stateId- numeric statepixiObj- link to a raw objectparentGameObject- link to the parentscene- link to the scene_proxy_- link to the proxy that contains implementation ofGameObjectinterfaceasContainer()- casts itself toECS.ContainerasParticleContainer()- casts itself toECS.ParticleContainerasXYZ()- casts itself to any class from the list of PIXI containers (throws an error if the casting is not possible)addComponent()- adds a new componentfindComponentByName()- finds a component by its nameremoveComponent()- removes a componentassignAttribute()- adds a new attribute to the hashmapgetAttribute()- gets an attribute by its keyremoveAttribute()- removes an existing attributeaddTag()- adds a tag to the set of tagsremoveTag()- removes a taghasTag()- returns true if given tag is in the setsetFlag()- sets a bit-flagresetFlag()- resets a bit-flaghasFlag()- returns true if given bit-flag is setinvertFlag()- inverts given bit-flagdetach()- detaches object from the scene but doesn't destroy it from PIXIdestroy()- destroy the object from the scene and from inner PIXI collections, and removes all of its componentsdestroyChildren()- destroys all children
let newObject = new ECS.Sprite('warrior', warriorTexture);
// we can store any number of attributes of any type
newObject.assignAttribute('speed', 20);
// we can store as many tags as we want
newObject.addTag('projectile');
// we can store flags within a range of 1-128
newObject.setFlag(FLAG_COLLIDABLE);
// a numeric state for a simple
newObject.stateId = STATE_MOVING;
Lifecycle
- objects are added to the game scene instantly
- when an object is attached to the scene, the scene will invoke the update loop upon it (it's being called recursively)
- if the object is detached, it will be removed from the game scene but it will not be destroyed
- detached objects can be re-added to the scene
- if the object is destroyed, it can no longer be used

Scene
- serves as a message bus and scene manager

app- link to thePIXI.Applicationname- name of the scenestage- root game object, derived fromPIXI.ContainercurrentDelta- current delta timecurrentAbsolute- current game timecallWithDelay(number, function)- invokes a function with a certain delayaddGlobalComponent(cmp)- adds a global component (attached to the stage)findGlobalComponentByName(name)- finds a global component by nameremoveGlobalComponent(component)- removes a global componentassignGlobalAttribute(name, attr)- assigns a global attribute to the stagegetGlobalAttribute(name)- gets a global atribute by nameremoveGlobalAttribute(string)- removes a global attributefindObjectById(id)- finds objects by idfindObjectsByQuery(query)- finds objects that meet conditions in the queryfindObjectsByName(name)- finds objects by namefindObjectByName(name)- gets the first object of given namefindObjectsByTag(tag)- finds objects that have given tagfindObjectByTag(tag)- gets the first object that has given tagfindObjectsByFlag(flag)- finds objects that have given flag setfindObjectByFlag(flag)- gets the first object that has a given flag setfindObjectsByState(state)- finds objects by numeric statefindObjectByState(state)- gets the first object that has a numeric state setsendMessage(message)- sends a generic message- it's better to send message from within components (the message will carry their id)
clearScene(config)- erases the whole scene
Scene querying
let droids = scene.findObjectsByTag('droid');
let charged = scene.findObjectsByFlag(FLAG_CHARGED);
let idle = scene.findObjectsByState(STATE_IDLE);
let chargedIdleDroids = scene.findObjectsByQuery({
ownerTag: 'droid',
ownerFlag: FLAG_CHARGED,
ownerState: STATE_IDLE
});
Delayed invocation
- don't use
setInterval()norsetTimeout(), as those two methods are invoked from the browser's event loop - if you want something to happen at a delay, you can use
scene.callWithDelay()instead, which is invoked at the end of the update loop - example: clear the whole scene after 3 seconds
// invoked from within a component
this.scene.callWithDelay(1000, () => this.scene.clearScene());
Messaging
Messageis an crate for inter-component communication- every component contains method
sendMessage(action, data) - we can also use
scene.sendMessage(Message)to send a message from outside a component - in order to receive messages of a given type, the component first needs to register itself via
subscribe(action) - all messages are handled in
OnMessage()of their respective handlers- if the
OnMessage()handler returns a value, it will be collected in theresponsesstructure
- if the
- if any component sets
expired = true, the message will not be passed any furter

Example: Finish a component by a message
class Sender extends ECS.Component {
onInit() {
this.fixedFrequency = 1;
}
onFixedUpdate() {
this.sendMessage('RECEIVER_FINISH');
}
}
class Receiver extends ECS.Component {
onInit() {
this.subscribe('RECEIVER_FINISH');
}
onMessage(msg: ECS.Message) {
if(msg.action === 'RECEIVER_FINISH') {
this.finish(); // will be removed from the scene instantly
}
}
}
Built-in messages
ANY- gets all messages (good for debugging)OBJECT_ADDED- object was added to the sceneOBJECT_REMOVED- object was removedCOMPONENT_ADDED- component was added to an objectCOMPONENT_DETACHED- component was detached from the scene (along with its owner)COMPONENT_REMOVED- component was removedATTRIBUTE_ADDED- attribute was added (sent only whennotifyAttributeChanges = true)ATTRIBUTE_CHANGED- attribute has changed (sent only whennotifyAttributeChanges = true)ATTRIBUTE_REMOVED- attribute was removed (sent only whennotifyAttributeChanges = true)STATE_CHANGED- state of an object has changed (sent only whennotifyStateChanges = true)FLAG_CHANGED- flag of an object has changed (sent only whennotifyFlagChanges = true)TAG_ADDED- tag was added to an object (sent only whennotifyTagChanges = true)TAG_REMOVED- tag was removed from an object (sent only whennotifyTagChanges = true)SCENE_CLEAR- the whole scene was erased
Example: Collect new objects by messaging pattern
class TreeCollector extends ECS.Component {
trees: ECS.Container[] = [];
onInit() {
this.subscribe('OBJECT_ADDED');
}
onMessage(msg: ECS.Message) {
if (msg.action === 'OBJECT_ADDED' && msg.gameObject.hasTag('TREE')) {
trees.push(msg.gameObject);
}
}
}
Built-in components and tools
Builder
- a versatile builder for all types of game objects

anchor()- set an anchorvirtualAnchor()- sets an anchor only virtually to calculate positionsrelativePos()- relative position on the screen within[0, 1]rangelocalPos()- local positionglobalPos()- global positionscale()- local scalewithAttribute()- adds an attributewithComponent()- adds a componentwithFlag()- adds a flagwithState()- adds a statewithTag()- adds a tagwithParent()- sets a parentwithChild()- sets a child BuilderwithName()- sets a nameasContainer()- sets the target object as a containerasGraphics()- sets the target object as graphicsasXYZ()- sets the target object as XYZ (anything from PIXI object collection)buildInto()- puts the data into an existing objectbuild()- builds a new objectclear()- clears data
new ECS.Builder(scene)
.relativePos(0.5, 0.92)
.anchor(0.5, 1)
.withAttribute(Attributes.RANGE, 25)
.withFlag(FLAG_COLLIDABLE)
.withFlag(FLAG_RANGE)
.withState(STATE_IDLE)
.withComponent(new TowerComponent())
.withComponent(new AimControlComponent())
.withComponent(new ProjectileSpawner())
.withName('tower')
.asSprite(PIXI.Texture.from(Assets.TEX_TOWER))
.withParent(rootObject)
.build();
Chain Component
- very powerful implementation of chain-of-commands
- every action is bound to the game update loop - the component udpates it inner state and invokes commands only when it's its turn

// displays a sequence of fancy rotating texts whilst in the bonus mode
this.owner.addComponent(new ChainComponent()
.beginWhile(() => this.gameModel.mode === BONUS_LEVEL)
.beginRepeat(4)
.waitFor(() => new RotationAnimation(0,360))
.waitFor(() => new TranslateAnimation(0,0,2,2))
.call(() => textComponent.displayMessage('BONUS 100 POINTS!!!'))
.call(() => soundComponent.playSound('bonus'))
.endRepeat()
.endWhile()
.call(() => viewComponent.removeAllTexts()));
// changes background music every 20 seconds
this.owner.addComponent(new ChainComponent()
.waitForMessage('GAME_STARTED')
.beginWhile(() => this.scene.stage.hasFlag(GAME_RUNNING))
.waitTime(20000)
.call(() => this.changeBackgroundMusic())
.endWhile()
Functional component
- a generic component that serves as a wrapper for simple functions

new ECS.FuncComponent('view')
.setFixedFrequency(0.1) // 1 update per 10 seconds
.doOnMessage('UNIT_EXPLODED', (cmp, msg) => cmp.playSound(Sounds.EXPLOSION))
.doOnMessage('UNIT_SPAWNED', (cmp, msg) => cmp.displayWarning(Warnings.UNIT_RESPAWNED))
.doOnFixedUpdate((cmp, delta, absolute) => cmp.displayCurrentState())
Key-Input Component
- a simple keyboard handled that only stores pressed keys
- doesn't send any messages, it has to be polled manually
// Factory.ts
initGame(scene: ECS.Scene) {
...
// here we need to add the KeyInputComponent globally
scene.addGlobalComponent(new KeyInputComponent());
...
}
// CannonInputController.ts
export class CannonInputController extends CannonController {
onUpdate(delta: number, absolute: number) {
// assuming that we added this component to the stage
let cmp = this.scene
.findGlobalComponentByName<KeyInputComponent>(ECS.KeyInputComponent.name);
if (cmp.isKeyPressed(ECS.Keys.KEY_LEFT)) {
this.turnLeft();
}
if (cmp.isKeyPressed(ECS.Keys.KEY_RIGHT)) {
this.turnRight();
}
}
}
Pointer-Input Component
- a global pointer handler
- PIXI has a built-in support for mouse events; this component handles mouse/pointer events for the canvas as a whole
- unlike
Key-Input Component, this one is using messaging pattern to notify the observers - the component handles both a mouse and a pointer
- config
- you need to explicitly configure which events should be captured
handleClickwill capture down/release actions
// add component
obj.addComponent(new ECS.PointerInputComponent( {
handleClick: false,
handlePointerDown: true,
handlePointerOver: true,
handlePointerRelease: true,
}));
- then, you can subscribe for following messages (you can find the enum in
ECS.PointerMessages):pointer-tappointer-downpointer-overpointer-release
Virtual-Gamepad Component
- a simple gamepad that extends
KeyInputComponentand translates clicks to keys - if you replace your
KeyInputComponentwithVirtualGamepadComponent, your game shouldn't notice the difference - config
- you need to provide a mapper to the keys
- if you omit certain keys, respective buttons will not render
this.engine.scene.addGlobalComponent(new ECS.VirtualGamepadComponent({
KEY_UP: ECS.Keys.KEY_UP,
KEY_DOWN: ECS.Keys.KEY_DOWN,
KEY_LEFT: ECS.Keys.KEY_LEFT,
KEY_RIGHT: ECS.Keys.KEY_RIGHT,
KEY_A: ECS.Keys.KEY_SPACE,
KEY_B: ECS.Keys.KEY_ENTER,
KEY_X: ECS.Keys.KEY_ALT,
KEY_Y: ECS.Keys.KEY_SHIFT
}));
- this being configured, the scene will contain a gamepad rendered on the top

Vector
- helper class for vectors

Responsive mode
- if you want your game render in full-screen mode, scaling with the browser window, you have 2 options:
- 1) set
resizeToScreentotruewhile initializing the engine - 2) add
?responsivequery string
- 1) set
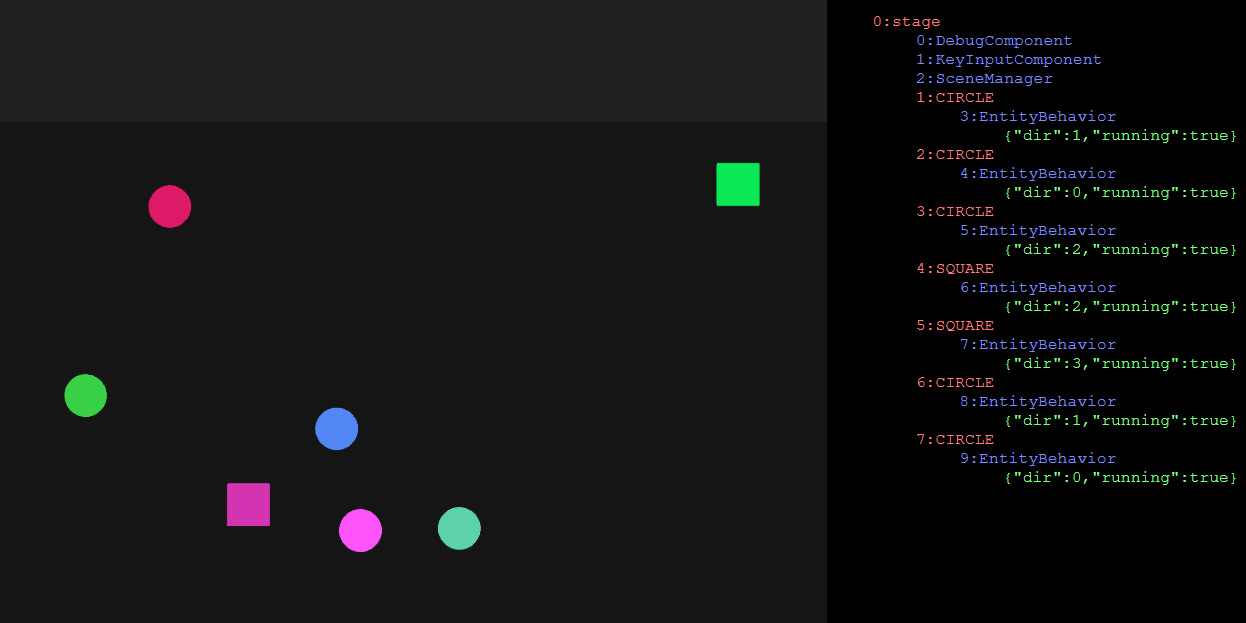
Debug Component
- debug component will attach a debugging panel next to the canvas
- three ways:
- 1) add
DebugComponentto the stage - 2) add
?debugquery string - 3) set
debugEnabledtotruewhile initializing the engine
- 1) add